
In the realm of professional photography and cinematography, rectilinear lens effect stands as a cornerstone of architectural and landscape imagery, delivering straight lines that remain perfectly straight – even at the widest angles. Unlike their fisheye counterparts, rectilinear lenses correct barrel distortion to maintain natural perspective, making them indispensable for photographers who demand geometric precision in their work.
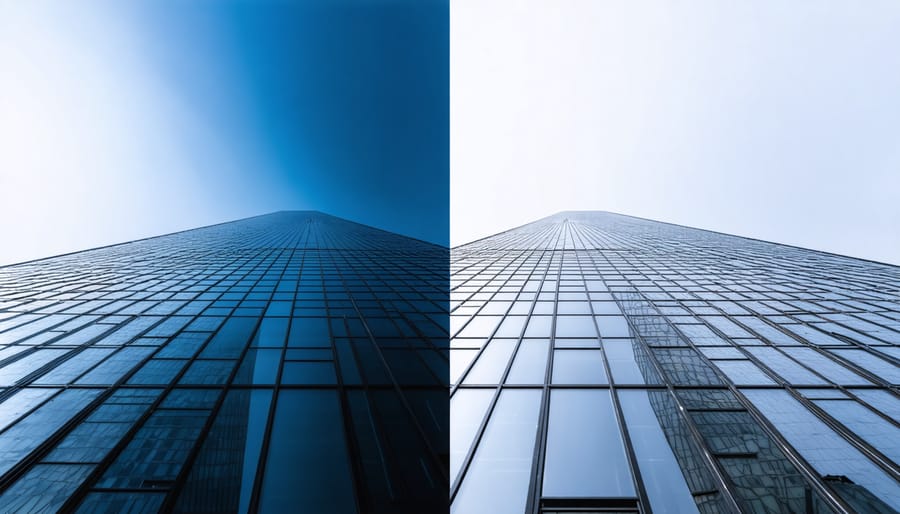
Picture a towering skyscraper photographed with a standard wide-angle lens, its edges bowing outward like a barrel. Now imagine that same building captured through a rectilinear lens – its vertical lines razor-straight from base to pinnacle, exactly as the human eye perceives them. This mathematical precision in image projection has made rectilinear lenses the go-to choice for serious architectural photographers and cinematographers who require true-to-life spatial relationships in their compositions.
The magic of rectilinear correction lies in its ability to preserve perspective while maintaining straight lines parallel to the frame’s edges, offering a natural view of the world that feels both expansive and accurate. Whether you’re shooting urban landscapes, interior spaces, or precise documentary work, understanding the rectilinear lens effect opens up new possibilities for creating visually striking images that maintain architectural integrity.
The Science Behind Rectilinear Lenses
Straight Lines Stay Straight
One of the most remarkable features of rectilinear lenses is their ability to maintain straight lines as straight in the final image. Unlike fisheye or other specialized lenses that can bend or distort linear elements, rectilinear lenses preserve the geometric accuracy of the scene before you. This is particularly valuable when photographing architecture, interiors, or any subject where straight lines are crucial to the composition.
Think of photographing a tall building: with a rectilinear lens, the vertical edges of the building remain parallel and straight, just as our eyes perceive them. This geometric precision is achieved through complex optical designs that correct for barrel and pincushion distortion, ensuring that light rays maintain their relative positions as they pass through the lens.
For photographers shooting cityscapes or architectural details, this characteristic is invaluable. It means you won’t need to spend time in post-processing correcting bent lines or warped perspectives. The natural preservation of straight lines also helps maintain the professional look that clients often expect, especially in commercial and architectural photography where accuracy is paramount.
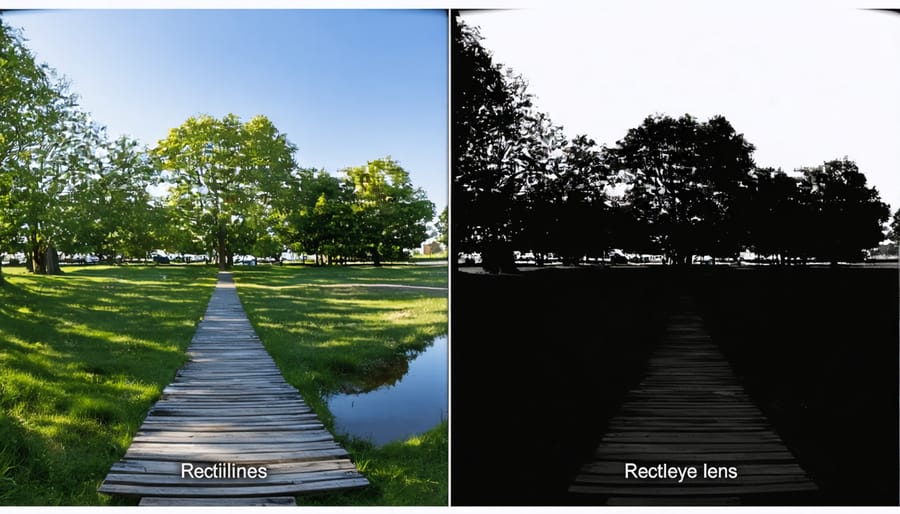

Understanding Distortion Control
Rectilinear lenses achieve their distortion-free images through careful optical design that maintains straight lines as straight, regardless of their position in the frame. This is accomplished through a complex arrangement of lens elements that work together to correct barrel and pincushion distortion – the two most common types of geometric distortion in photography.
The key to this correction lies in the precise calculation of how light rays bend as they pass through each element of the lens. Engineers design these elements to counteract the natural tendency of wide-angle lenses to curve straight lines. Think of it as a series of corrections, where each lens element slightly adjusts the light path to ensure that what’s straight in real life remains straight in your final image.
Modern rectilinear lenses often incorporate aspherical elements and specialized glass types that help minimize distortion while maintaining sharpness and clarity. This is particularly important in architectural and real estate photography, where straight lines are crucial for maintaining the natural appearance of buildings and interiors.
The trade-off for this distortion control is that objects near the edges of the frame may appear larger than those in the center, though their geometric shapes remain true to life.
Cinematic Applications
Architecture and Interior Shots
Architecture and interior photography presents unique challenges when it comes to capturing straight lines and maintaining proper perspective. Rectilinear lenses shine in these scenarios by ensuring vertical and horizontal lines remain true to their real-world appearance, making them essential tools for professionals in this field.
When photographing buildings, a rectilinear lens helps avoid the barrel or pincushion distortion that might otherwise make structures appear warped or unnatural. This is particularly crucial when shooting tall buildings, where converging lines can create an unsettling effect. By combining rectilinear lenses with proper cinematic lens techniques, photographers can achieve professional-grade architectural shots that maintain geometric accuracy while still conveying artistic vision.
For interior photography, these lenses excel at capturing rooms in their true proportions. Whether you’re shooting real estate listings or documenting interior design projects, rectilinear lenses help maintain the authentic spatial relationships between walls, floors, and ceilings. This accuracy is essential for commercial work where clients expect faithful representations of their spaces.
To maximize results, position your camera parallel to the main walls and ensure it’s perfectly level. This approach, combined with a rectilinear lens, will help you capture interiors and architecture with minimal distortion and maximum impact. Remember that even slight camera tilts can introduce unwanted perspective changes, so using a tripod and level is highly recommended.

Dramatic Landscape Compositions
When composing dramatic landscapes with a rectilinear lens, you have the unique advantage of capturing expansive scenes while maintaining natural-looking straight lines and proportions. Start by positioning strong vertical elements, like buildings or trees, near the edges of your frame – these will remain perfectly straight thanks to the lens’s distortion-free characteristics. This approach, combined with professional lighting techniques, creates powerful architectural and landscape compositions.
Consider the rule of thirds when framing your shot, but don’t be afraid to break it intentionally. The rectilinear lens’s ability to maintain perspective makes it excellent for emphasizing leading lines in your composition. Try positioning yourself to capture roads, fences, or shorelines that draw the viewer’s eye naturally through the frame.
For mountain landscapes, position your camera slightly below eye level to emphasize height while maintaining natural proportions. This technique works particularly well during golden hour when shadows can add depth to your composition. When photographing cityscapes, align your camera parallel to building facades to maximize the lens’s natural ability to keep vertical lines straight.
Remember to use foreground elements strategically – they’ll appear properly proportioned relative to the background, creating a natural sense of depth without the distortion typically associated with wide-angle lenses. This helps maintain the viewer’s connection with the scene while still capturing its grandeur.
Choosing the Right Rectilinear Lens
Wide-Angle vs. Ultra-Wide Options
When exploring rectilinear lenses, you’ll encounter two main categories that dramatically affect your image perspective: wide-angle and ultra-wide-angle options. Wide-angle lenses, typically ranging from 35mm to 24mm, offer a natural-looking wide view while maintaining relatively minimal distortion. These lenses are perfect for architectural photography and creating in-camera effects that don’t overwhelm the viewer.
Ultra-wide lenses, however, push the boundaries further, covering focal lengths from 24mm down to around 12mm. These lenses deliver an expansive field of view while keeping straight lines straight – a defining characteristic of rectilinear designs. While they maintain geometric accuracy, they do introduce perspective distortion, making objects near the edges appear stretched or elongated compared to the center of the frame.
The choice between wide and ultra-wide often depends on your creative vision and shooting environment. Wide-angle lenses (28-35mm) excel in documentary and street photography, offering a natural perspective that doesn’t immediately announce itself as “wide.” They’re also more forgiving when it comes to keeping vertical lines parallel, especially in architectural shots.
Ultra-wide options (24mm and wider) make a bold statement, dramatically emphasizing foreground elements while pushing backgrounds into a seemingly infinite distance. This effect can be particularly powerful for landscape photography or creating a sense of scale in tight spaces. However, they require more careful composition to avoid unwanted distortion, especially when photographing people near the frame edges.
Remember that both options maintain straight lines, unlike their fisheye counterparts, making them invaluable tools for professional architectural and interior photography where geometric accuracy is crucial.
Budget vs. Premium Choices
When it comes to rectilinear lenses, the price range can vary significantly, from around $200 to well over $2,000. Understanding what you get at different price points can help you make an informed decision that matches your needs and budget.
In the budget category ($200-500), you’ll find lenses from manufacturers like Samyang/Rokinon that offer good rectilinear correction and decent build quality. These lenses typically feature manual focus, which might require more skill to use effectively. While they may lack weather sealing and sophisticated coatings, they can still deliver impressive results when used skillfully.
Mid-range options ($500-1,200) from brands like Tokina and Sigma offer significant improvements in build quality and optical performance. You’ll find features like autofocus, better flare resistance, and sharper edge-to-edge performance. These lenses often represent the sweet spot of value for enthusiast photographers.
Premium choices ($1,200+) from manufacturers like Canon, Nikon, and Sony showcase the pinnacle of rectilinear lens technology. You’re paying for superior edge sharpness, better performance in challenging lighting conditions, and robust weather sealing. These lenses typically offer faster maximum apertures, more sophisticated optical designs, and better chromatic aberration control.
However, higher price doesn’t always mean better results for your specific needs. A skilled photographer can create stunning images with budget options, while expensive glass won’t automatically improve poor technique. Consider factors like your shooting style, typical subjects, and whether features like weather sealing or autofocus are essential for your work before making your investment.
Common Pitfalls and Solutions
Managing Edge Distortion
Edge distortion in rectilinear lenses can be effectively managed with several practical techniques. The most straightforward approach is to maintain a comfortable distance from your subject, especially when shooting with wider focal lengths. As a general rule, keeping key elements away from the frame’s edges will help minimize unwanted stretching effects.
Composition plays a crucial role in managing edge distortion. Consider placing important subjects closer to the center of the frame, where distortion is minimal. When photographing architecture or interiors, try positioning yourself so that major vertical lines fall within the middle third of the frame rather than at the edges.
During post-processing, you can further reduce edge distortion using lens correction tools found in most editing software. These tools often come with pre-loaded profiles for specific lens models, making corrections more accurate and easier to apply. Manual adjustments to perspective and distortion controls can also help fine-tune the final image.
Another effective strategy is to slightly overshooting your scene and cropping in post-production. This technique allows you to eliminate the most distorted edges while maintaining your desired composition. Some photographers even deliberately compose with this crop in mind, knowing they’ll trim away the problematic areas later.
For critical architectural or product photography, consider using tilt-shift lenses, which offer superior control over perspective and minimize edge distortion by design.
Composition Tips
When working with rectilinear lenses, mastering visual composition principles becomes even more crucial due to the lens’s unique characteristics. Start by positioning strong vertical elements, like buildings or trees, near the frame edges to maximize the lens’s ability to maintain straight lines. This placement helps create a powerful sense of scale and perspective.
Consider the rule of thirds, but be mindful that rectilinear lenses can make subjects near the edges appear slightly larger. Use this effect to your advantage by placing important elements slightly closer to the center than you typically would. When photographing architecture, position yourself to capture parallel lines running through your frame – this emphasizes the lens’s ability to maintain geometric accuracy.
For landscape photography, keep your horizon line straight and centered if possible, as any slight tilt will be more noticeable with a rectilinear lens. When photographing interiors, position yourself in corners or doorways to capture maximum space while maintaining natural-looking proportions.
Pay special attention to foreground elements, as they can help create depth without the distortion typically associated with wide-angle lenses. If photographing people, keep them away from the edges of the frame where stretching might occur, unless you’re deliberately using this effect for creative impact.
Remember that negative space becomes particularly powerful with rectilinear lenses, helping to emphasize the grandeur of architectural subjects while maintaining their natural proportions.
The rectilinear lens effect remains a powerful tool in the photographer’s arsenal, offering a unique combination of technical precision and creative possibilities. Throughout this exploration, we’ve seen how these lenses maintain straight lines and natural perspectives, making them invaluable for architectural photography, landscape work, and professional cinematography.
Remember that while rectilinear lenses excel at correcting distortion, they’re not always the best choice for every situation. Their effectiveness depends on various factors, including your subject matter, shooting environment, and creative vision. For architectural work and situations where maintaining geometric accuracy is crucial, they’re often the optimal choice. However, for creative applications where some distortion might enhance the image, you might want to explore other options.
For photographers just starting with rectilinear lenses, we recommend beginning with a standard wide-angle lens (24-35mm) before moving to ultra-wide options. This allows you to develop a solid understanding of how these lenses behave and how to work with their characteristics effectively. Pay particular attention to composition and perspective, as these elements become increasingly critical when working with wider angles.
As you continue your photographic journey, experiment with different focal lengths and shooting distances to find the sweet spot that works best for your specific needs. Remember that successful rectilinear photography often comes down to careful planning, proper technique, and a thorough understanding of your equipment’s capabilities.






















