Motion-activated cameras revolutionize wildlife photography and security monitoring by capturing precise moments without constant surveillance. Master your action camera settings to freeze split-second movements, from soaring eagles to lightning strikes, with unparalleled clarity. These sophisticated devices combine advanced sensor technology with intelligent triggering mechanisms, transforming unpredictable moments into stunning photographs.
Modern motion detection systems analyze multiple zones within the frame, distinguishing between ambient movement like swaying branches and genuine subject activity. This technological breakthrough enables photographers to document elusive wildlife behavior, capture security footage with pinpoint accuracy, and explore creative possibilities in high-speed photography – all while conserving battery life and storage space.
Whether you’re a wildlife enthusiast tracking nocturnal animals or a security professional seeking reliable surveillance solutions, motion-activated cameras offer precision, reliability, and unprecedented creative control. Their evolution from simple trigger devices to sophisticated imaging tools has opened new frontiers in both professional photography and everyday monitoring applications.
How Motion Detection Works in Action Cameras
Sensor Types and Technologies
Modern motion-activated cameras employ several sophisticated types of camera sensor technology to detect movement. The most common is the Passive Infrared (PIR) sensor, which detects changes in heat signatures when objects or beings move through its field of view. These sensors are particularly effective for wildlife photography and security applications.
Another popular option is the Active Motion Sensor, which uses microwave or ultrasonic technology to emit waves and measure their reflection off moving objects. This type excels in challenging lighting conditions and can detect subtle movements that heat-based sensors might miss.
Some advanced cameras combine multiple sensor types in what’s called a dual-technology system. For instance, pairing PIR with microwave sensors reduces false triggers while ensuring reliable activation when needed. Image-based motion detection is also gaining popularity, where the camera’s processor analyzes consecutive frames to identify movement, offering precise detection especially in controlled environments.
The choice of sensor type largely depends on your specific needs – PIR for general wildlife photography, active sensors for sports capture, or dual-technology for security applications.
Trigger Sensitivity and Range
The effectiveness of a motion-activated camera largely depends on its trigger sensitivity and detection range settings. Most modern cameras offer adjustable sensitivity levels, typically ranging from low to high, allowing you to fine-tune the camera’s response to movement. Higher sensitivity settings are ideal for capturing small, quick subjects like birds or insects, while lower settings work better for larger subjects and help prevent false triggers from wind-blown vegetation.
Detection range varies significantly between models, with most consumer-grade motion cameras covering 30-50 feet effectively. Professional models can detect movement up to 100 feet or more. The detection angle is equally important, with wider angles (often 90-120 degrees) providing better coverage but potentially increasing false triggers.
For optimal performance, consider your specific environment and subject matter. Urban settings might require shorter ranges and lower sensitivity to avoid constant triggering from passing cars or pedestrians. Wildlife photography, on the other hand, often benefits from higher sensitivity and longer detection ranges. Remember that lighting conditions can affect the camera’s trigger response, with most devices performing better in good light than in low-light situations.
Creative Applications and Shooting Techniques
Wildlife Photography
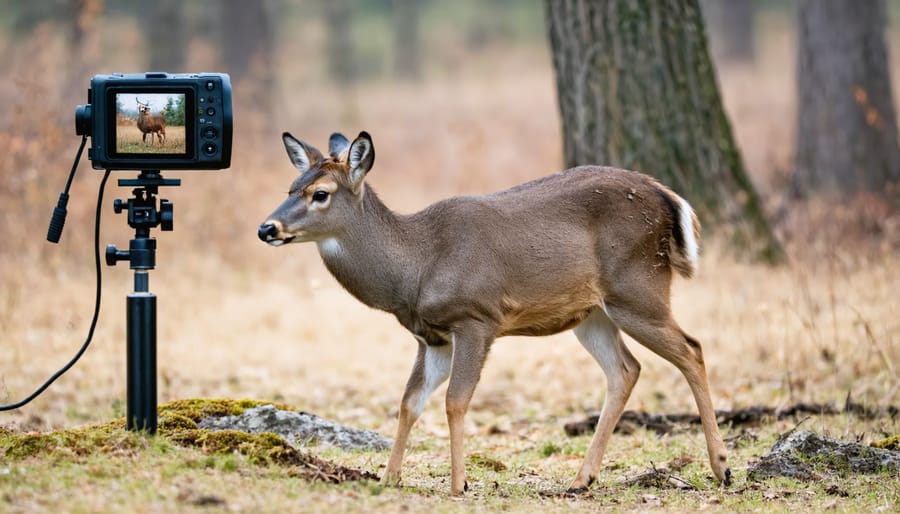
Motion-activated cameras have revolutionized wildlife photography, allowing photographers to capture intimate moments of animal behavior without human presence. These devices excel at documenting nocturnal species, shy animals, and rare wildlife that might otherwise be impossible to photograph through traditional methods.
Setting up a motion-activated camera for wildlife requires careful consideration of animal patterns and habitats. Photographers typically position their cameras along game trails, near water sources, or in areas with clear signs of animal activity. The key is to mount the camera at an appropriate height and angle that matches your target species – lower for small mammals, higher for larger animals like deer or bears.
For optimal results, many wildlife photographers combine motion detection with infrared technology for night shooting. This approach prevents startling animals with visible flash while still capturing clear images in darkness. Some photographers also use multiple cameras to create comprehensive coverage of an area, increasing their chances of capturing unique behavioral sequences.
The real magic happens when you retrieve your camera and discover unexpected moments – a mountain lion stretching at dawn, a family of foxes playing, or perhaps a species never before documented in the area.

Sports and Action Shots
Motion-activated cameras have revolutionized sports photography, enabling photographers to capture split-second moments that might otherwise be missed. From a tennis player’s serve to a skateboarder’s mid-air flip, these cameras excel at freezing action in crisp detail.
Professional sports photographers often position multiple motion sensors around key areas of play. For instance, during basketball games, sensors near the hoop trigger cameras to capture dramatic dunks and rebounds. In track and field events, strategically placed sensors along the finish line ensure perfect timing for those photo-finish moments.
The technology really shines in extreme sports photography. When shooting activities like mountain biking or snowboarding, photographers can set up cameras along the course, letting motion sensors do the work while maintaining a safe distance. This approach not only ensures photographer safety but also allows for unique angles and perspectives that would be impossible to achieve manually.
For wildlife action shots, motion-activated cameras are invaluable. They can capture predator-prey interactions, birds in flight, or animals in their natural habitats without human presence affecting their behavior. The key to success lies in proper sensor sensitivity adjustment and careful positioning based on anticipated movement patterns.
To achieve the best results, photographers should consider factors like subject speed, lighting conditions, and the desired frame sequence. Many modern systems allow for customizable trigger delays and burst modes, ensuring you never miss the perfect moment of action.
Time-Lapse and Security
Motion-activated cameras excel in two particularly useful applications: creating dynamic time-lapse sequences and providing reliable security monitoring. For time-lapse projects, motion detection helps conserve storage space and battery life by capturing only meaningful changes in the scene. Whether you’re documenting construction progress or tracking wildlife behavior, these time-lapse photography techniques ensure you don’t miss crucial moments while eliminating redundant frames.
In security applications, motion activation serves as an efficient sentinel, recording only when movement occurs in the monitored area. This smart triggering system proves invaluable for home security, wildlife monitoring, and workplace surveillance. Modern motion-activated cameras often include features like zone selection, allowing you to specify areas where movement should trigger recording while ignoring others.
Many cameras now offer cloud integration, instantly uploading motion-detected events for remote viewing. This feature provides real-time notifications and peace of mind, whether you’re monitoring your property or capturing nature’s unexpected moments. Some advanced models even incorporate AI-powered detection to distinguish between different types of movement, such as separating human activity from animal movements or vehicle traffic.
Setting Up Motion Detection
Basic Configuration
Getting your motion-activated camera up and running starts with a few essential configuration steps. Begin by positioning your camera in a stable location with a clear view of the area you want to monitor. The ideal height is typically between 3-6 feet off the ground, ensuring the sensor can effectively detect movement in its field of view.
Next, access your camera’s settings menu to adjust the motion sensitivity. Start with a medium sensitivity setting – you can fine-tune this later based on your specific needs. Too high sensitivity might trigger false alerts from wind-blown leaves or small insects, while too low might miss important events.
Set your detection zone by defining the specific areas where you want the camera to monitor movement. Most modern motion-activated cameras allow you to create custom zones or mask certain areas to prevent unnecessary triggers. This is particularly useful in environments with regular background motion, like swaying trees or busy streets.
Configure your camera’s recording duration and delay time between captures. A typical starting point is 30 seconds of recording with a 10-second delay between triggers. This helps conserve battery life and storage space while ensuring you don’t miss important events.
Finally, test your setup by walking through the detection zone at various speeds and angles. This real-world testing helps verify that your camera captures motion effectively and allows you to make any necessary adjustments to the settings.
Advanced Settings and Tips
To get the most out of your motion-activated camera, delve into these advanced settings and optimization techniques. Start by adjusting the sensitivity threshold – lower settings work best for capturing larger subjects like wildlife, while higher sensitivity excels at detecting subtle movements like leaves rustling or small birds.
Consider customizing the detection zones by creating specific regions of interest. This helps eliminate false triggers from busy backgrounds or moving trees while focusing on critical areas where action is expected. Many modern cameras also offer enhanced low-light detection capabilities, which can be fine-tuned by adjusting the IR sensor’s range and sensitivity.
Pro tip: Set up your camera’s pre-trigger recording feature to capture moments just before motion is detected. A buffer of 2-3 seconds often makes the difference between catching the full action sequence and missing the crucial initial movement.
Battery optimization is crucial for extended deployments. Configure sleep mode intervals carefully – shorter intervals provide more responsiveness but drain battery faster. For optimal performance, consider using external power sources or solar panels for long-term installations.
Weather can affect motion detection accuracy, so adjust settings seasonally. Increase sensitivity during calm conditions and decrease it on windy days to prevent unnecessary triggers. Remember to regularly clean the sensor window and check the camera’s positioning to maintain reliable detection.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Battery Life Management
Maximizing battery life is crucial for motion-activated cameras, especially when deployed in remote locations or during extended shooting sessions. To get the most out of your camera’s battery, start by adjusting the motion sensitivity settings to prevent unnecessary triggers from wind-blown vegetation or distant movement. Most cameras allow you to customize the detection zone and sensitivity level – finding the right balance is key.
Consider using lithium batteries instead of standard alkaline ones, as they perform better in extreme temperatures and typically last longer. For cameras with rechargeable batteries, invest in high-quality cells with a higher mAh rating for extended operation time.
The recording duration and image quality settings significantly impact battery consumption. While it’s tempting to opt for the highest resolution, consider whether 1080p might suffice instead of 4K for your specific needs. Similarly, adjust the clip length to capture only essential moments – a 10-second recording often works better than a 30-second one for most situations.
Weather conditions also affect battery performance. In cold environments, batteries drain faster, so consider using insulated battery compartments or external battery packs. Some photographers even rotate between two sets of batteries, keeping the spare set warm and ready for swap.
Finally, regularly clean the motion sensor and ensure proper positioning of your camera. A dirty sensor or poor placement might trigger unnecessary recordings, leading to premature battery drain.
False Triggers and Adjustments
False triggers can be frustrating when using motion-activated cameras, but understanding their common causes helps you make the necessary adjustments. Wind-blown vegetation is often the biggest culprit, causing unnecessary recordings and draining battery life. To combat this, try adjusting your camera’s sensitivity settings and carefully considering the camera’s placement relative to moving foliage.
Temperature changes can also fool your camera’s sensors. On hot days, rising heat waves might trigger false activations, while rapid temperature fluctuations during dawn and dusk can cause similar issues. Many advanced cameras offer temperature compensation features that you can fine-tune to minimize these false triggers.
The detection zone is crucial for accurate activation. Most cameras allow you to adjust both the detection range and angle. Start with a smaller detection zone and gradually increase it until you find the sweet spot for your specific needs. Some cameras also offer zone masking, letting you block out areas prone to false triggers, like busy streets or moving branches.
Light conditions can impact sensor performance. Strong shadows, rapid light changes, or reflective surfaces might trigger your camera unnecessarily. Consider using the camera’s scheduling feature to activate only during specific times, or adjust the sensor’s light sensitivity if your model offers this option.
Remember that finding the right balance often requires experimentation and patience. Keep a log of false triggers to identify patterns and make informed adjustments to your settings.
Motion-activated cameras have revolutionized the way we capture dynamic moments, and their continued evolution promises even more exciting possibilities ahead. From wildlife photography to security applications, these versatile devices have proven their worth across numerous scenarios, making them indispensable tools for both amateur and professional photographers.
As we’ve explored throughout this article, the key advantages of motion detection in action cameras include battery conservation, storage optimization, and the ability to capture otherwise impossible shots. The technology has matured significantly, offering increasingly sophisticated features like AI-powered subject recognition, advanced triggering mechanisms, and improved low-light performance.
Looking ahead, we can expect motion detection technology to become even more refined. Emerging trends point toward enhanced AI capabilities that can predict movement patterns, better false-trigger prevention, and seamless integration with smart home systems. The miniaturization of components will likely lead to smaller, more efficient cameras without compromising on features or performance.
For photographers and enthusiasts considering motion-activated cameras, the future is bright. Whether you’re documenting wildlife behavior, creating time-lapse sequences, or securing your property, these devices offer unprecedented opportunities for capturing meaningful moments. As the technology continues to advance, we can look forward to even more innovative features that will push the boundaries of what’s possible in motion-activated photography.
Remember that success with these devices comes from understanding both their capabilities and limitations, and taking time to master their settings for your specific needs.